Last Updated on July 30, 2025 by Henry James
First aid is one of the most valuable skills a person can acquire, yet traditional training methods often struggle to keep learners fully engaged. Lectures, slideshows, and repetitive drills, while necessary, can feel monotonous and disconnected from real-life situations. This is where gamification—a learning method that applies game design elements to non-game contexts—offers a fresh and powerful alternative.
Gamification transforms passive learning into active problem-solving, bringing energy and motivation to first aid education. Whether used in classrooms, workplace training sessions, or community programs, this approach is proving to be both enjoyable and effective. But how exactly does it work, and why does it matter for something as serious as first aid?
What is Gamification in Learning?
Gamification involves integrating game-like features such as points, badges, levels, challenges, and narratives into educational settings. The goal is to increase engagement, motivation, and retention of knowledge by appealing to our innate love for play and achievement.
In first aid training, gamification can involve:
- Scenario-based simulations
- Interactive quizzes with scores and rewards
- Role-playing challenges
- Time-based tasks or competitions
- Leaderboards for team or class performance
By turning lessons into interactive experiences, gamification keeps learners involved, encourages critical thinking, and fosters better long-term retention of first aid protocols.
Why Gamify First Aid Training?
Traditional first aid courses often rely on rote memorization, which may not stick when stress levels are high. Gamification adds realism, emotion, and repetition in a non-threatening format, which prepares individuals more effectively for real emergencies.
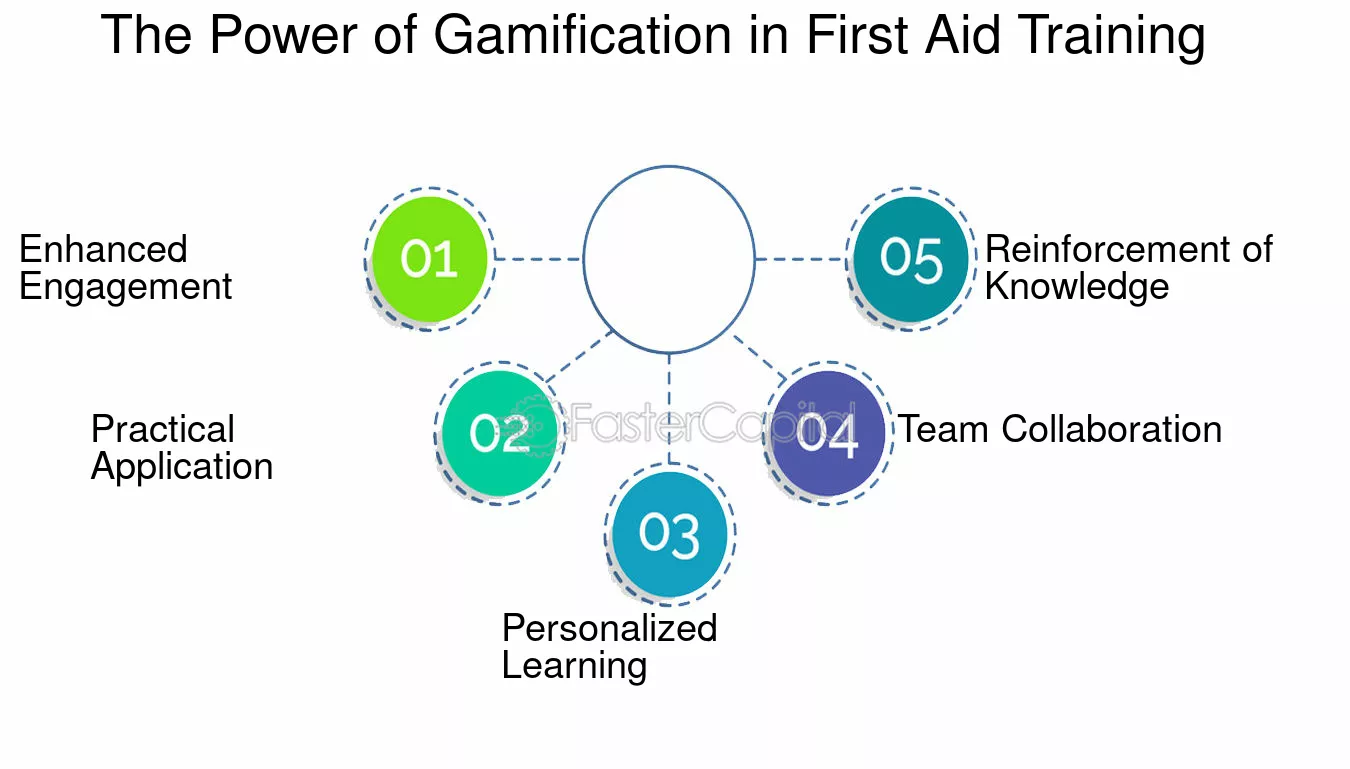
Benefits of gamified first aid training:
- Enhanced engagement: Learners are more attentive and active during sessions.
- Improved memory retention: Repetition through games reinforces key concepts.
- Immediate feedback: Participants can correct mistakes in real-time.
- Lowered anxiety: Games create a safe space for trial and error.
- Team collaboration: Group-based activities build communication and coordination skills.
This method has been especially effective among younger learners, workplace teams, and community volunteers who might not thrive in conventional classroom environments.
Examples of Gamified First Aid Methods
Gamification doesn’t have to involve fancy technology (though it can). Here are several practical methods that have shown strong results:
1. First Aid Escape Rooms
Participants must “escape” a room by solving a series of first aid-related puzzles. For example, identifying how to treat a victim in cardiac arrest or interpreting symptoms of heatstroke could unlock clues to progress.
This combines learning with adventure and simulates time-sensitive decision-making.
2. Simulation Apps and Virtual Reality
Digital platforms allow users to walk through emergencies on-screen or in VR. Scenarios range from administering CPR on a virtual victim to navigating triage after a disaster.
These tools are growing rapidly in popularity and are often linked with formal certification programs, including those like Carleton University’s First Aid and CPR training, which integrate tech-based learning with hands-on sessions.
3. Card and Board Games
Custom card decks or board games can be developed where players match symptoms with treatments or race against a timer to simulate emergency response. Points are awarded for correct answers or successful team strategies.
This low-tech approach is cost-effective and easy to implement in schools and workshops.
4. Gamified Online Courses
Online platforms now offer point-based progress, quizzes, and badges for learners completing modules. Learners can track their development, compete with others, and review areas where they made errors.
A student who completed one such course shared how the “unlockable achievements” in the app helped them stay motivated during a self-paced program, even when distractions at home were high.
Interestingly, during one discussion of course delivery preferences, a learner mentioned how their first aid certificate program could have benefited from integrating such gaming elements—it was a side comment, but pointed out how traditional models may be missing opportunities for engagement.
Gamification and Different Age Groups
The great thing about gamification is its adaptability across all ages:
- Young children: Use songs, stories, and puppet shows to teach basic safety.
- Teens: Escape rooms, team challenges, and mobile quizzes keep them engaged.
- Adults: Simulations and scenario-based training appeal to real-world logic.
- Seniors: Memory games and role-play help reinforce procedures in a relaxed setting.
This flexibility allows instructors to tailor the experience to different audiences without compromising educational value.
Challenges of Gamifying First Aid Education
While gamification brings many advantages, it’s not without challenges:
- Balancing fun with seriousness: Emergencies are no joke, and training must reflect that.
- Ensuring accuracy: Games must still follow evidence-based guidelines and avoid misinformation.
- Resource requirements: Customizing and maintaining games may need additional time or tech investment.
- Instructor training: Facilitators must be comfortable guiding gamified sessions.
Addressing these issues means integrating games as a complement—not a replacement—for hands-on practice and traditional instruction.
Best Practices for Implementing Gamification in First Aid
To make the most of gamification:
- Define clear learning outcomes before designing any game element.
- Use scenarios grounded in real-life emergencies to enhance realism.
- Incorporate reflection time so learners can discuss what they did and why.
- Mix formats—combine digital tools, physical games, and group activities.
- Pilot-test games to ensure they are intuitive, educational, and relevant.
Collaboration between educators, emergency professionals, and instructional designers can create the most effective outcomes.
The Future of Gamified First Aid Training
As technology continues to evolve, gamified training will only become more immersive. Augmented reality (AR), AI-based feedback, and adaptive learning platforms will offer increasingly personalized first aid education. The future holds exciting possibilities where learners are coached by virtual instructors in real-time or complete missions that mirror actual emergency response duties.
But even as tools advance, the goal remains the same: to prepare people to save lives—confidently, competently, and compassionately.
Conclusion
Gamification has redefined how we teach and learn essential skills—and first aid is no exception. By making training interactive and engaging, we foster not only knowledge but also the confidence to act when it truly matters. From classrooms to community centers, incorporating gamified elements into first aid education bridges the gap between knowing what to do and being ready to do it.
And while traditional certification is still vital, integrating game-based learning ensures that more people enjoy the journey to preparedness—and remember what they’ve learned when it counts most.

Henry James is the humorist behind Haha Joks, a website where laughter reigns supreme. With a deep appreciation for wit and clever wordplay, Henry crafts and shares jokes that bring joy to readers of all ages. His mission is simple: to spread happiness, one joke at a time. Whether you’re looking for a quick giggle or a side-splitting laugh, Henry’s collection on Haha Joks is sure to deliver.